Top Gen AI Trends in Business in 2023
Generative AI is seeing a boom in all industries and sectors. Read to find some key trends being followed by savvy businesses using GenAI this year.
Key Takeaways
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI or Gen AI) is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on the creation of new, original content.
Generative AI technology operates on the principles of deep learning and neural networks. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are two popular generative model architectures.
The annual McKinsey global survey reported that there has been an “explosive” growth of Gen AI tools. Halfway through the year, even though Generative AI tools are not as widely available, there’s a huge range of experimentation in various sectors and industries already.
Some of the key trends being shown by businesses this year include the use of Generative AI to create innovative applications to boost productivity and customer experience, as well as build smoother workflows.
Existing GenAI architecture has also seen improvements. Moreover, there has been an increased flow of investments towards utilizing GenAI in business.
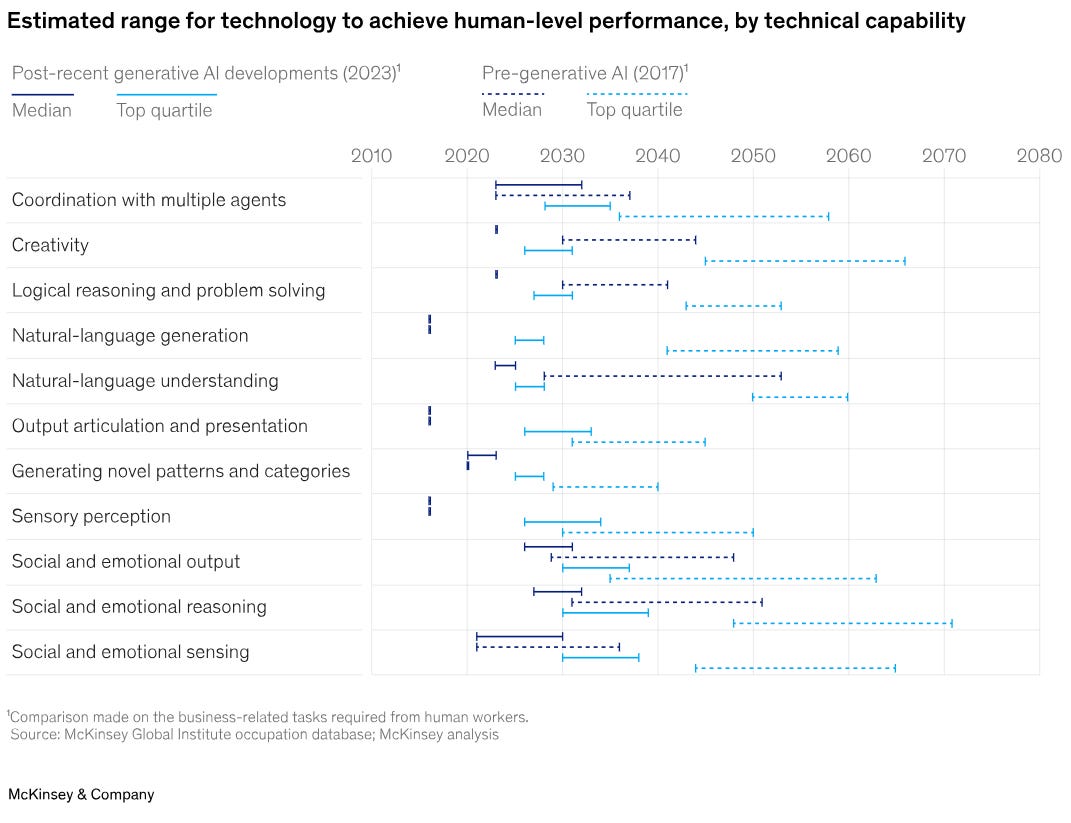
Savvy business leaders are already utilizing Generative AI in creative ways. But most of them also feel that the technology is highly underutilized, as demonstrated in the chart above. There’s room for innovation and increased application of GenAI, especially among smaller and midsized businesses.
This post is sponsored by Multimodal, an NYC-based startup setting out to make organizations more productive, effective, and competitive using generative AI.
Multimodal builds custom large language models for enterprises, enabling them to process documents instantly, automate manual workflows, and develop breakthrough products and services.
Visit their website for more information about transformative business AI.
In today's fast-paced business landscape, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer across industries. This year, one domain of AI has seen explosive growth and multiple applications: Generative AI. Across industries, Generative AI, particularly through large language models, is being harnessed to increase productivity, save time, and boost innovation.
Generative AI’s capacity to create new content, ranging from images and text to music and more, has opened up a realm of possibilities that was once the stuff of science fiction. In this article, we will take a look at some of the recent trends of using Generative AI by businesses across multiple industries and sectors. Additionally, we’ll also look at how small businesses can use GenAI without having to spend a fortune.
What is Generative AI?
Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI or Gen AI) is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on the creation of new, original content.
Unlike traditional AI systems that rely on pre-existing data patterns to make decisions or classifications (discriminative AI), Generative AI goes a step further by generating entirely new data that resembles, and in some cases, is indistinguishable from, real data.
Generative AI vs. Other AI Approaches
Unlike older “AI” systems that mainly focus on processing data, Generative AI systems focus on generating it. For example, while we could use older AI models to extract specific clauses from contracts, they can’t help us create new ones. That’s where Generative AI comes in.
(Note that we have some reservations about classifying prior models as AI. The definition of artificial intelligence evolves together with new advancements in the field, so some no longer consider non-generative models to be real AI.)
Besides generating formulaic text, such as contract clauses, Generative AI can also dream up new paintings, write original stories, or even generate realistic human faces that don't exist in the real world. Generative AI’s ability to create makes it a potent tool for various applications.
How Generative AI Models Work
Generative AI technology operates on the principles of deep learning and neural networks. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are two popular generative model architectures.
1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs consist of two neural networks—the generator and the discriminator—locked in a competitive game. The generator's role is to create synthetic data, while the discriminator's job is to distinguish between real and synthetic data. They continually improve their performance through this adversarial process, resulting in the generator producing increasingly realistic content over time. GANs have made headlines for their ability to generate lifelike images, deep fake videos, and even art.
2. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): VAEs are probabilistic models that learn to encode and decode data. They aim to find a lower-dimensional representation of the input data, allowing for the generation of new data points that adhere to the learned distribution. VAEs are often used in applications like image compression and data generation.
In essence, both GANs and VAEs leverage neural networks to create content that follows the patterns and structures observed in the training data. However, they approach this task from different angles, with GANs emphasizing competition and realism, while VAEs focus on probabilistic encoding and decoding.
Gen AI Trends in Business in 2023
This year, the annual McKinsey global survey showed an “explosive” growth of Gen AI tools. According to the report:
“Less than a year after many of these tools debuted, one-third of our survey respondents say their organizations are using gen AI regularly in at least one business function.”
Halfway through the year, even though Generative AI tools are not as widely available, there’s already a huge range of experimentation in various sectors and industries. Technical automation has reached a significant high across industries, which shows the unique potential of Generative AI systems.
Here are some of the top trends and ways Generative AI is being used in business.
1. Creative Applications in Multiple Industries
Generative AI applications in multiple industries have been wide-ranging and super innovative. Here are some great examples:
Midjourney and Stable Diffusion, two groundbreaking media-generation applications harnessed the power of virality on social media. Then ChatGPT was released, making GenAI super accessible and popular.
Generative writing applications have seen exponential growth too, capitalizing on the capabilities of language language models (LLMs). Jasper, powered by GPT-4, assists marketing copywriters in crafting compelling content.
With language models growing in sophistication, they've ventured into complex domains, such as legal text. Harvey now aids law and professional services firms by performing associate-level legal work, while Ironclad automates contract processes for in-house legal teams.
Generative AI's inherent creativity naturally extends into other creative fields. Runway redefines video production, generating, editing, and applying effects. Apps like Tome enable users to design beautiful, impactful presentations with just text prompts, elevating the art of communication at work.
Generative AI technology is creating diverse applications. Yes, it does remain largely inaccessible to smaller businesses at the same level as larger corporations. But the AI market is expanding quickly enough to reduce that gap.
Moreover, as foundation models are improved, things like simple fine-tuning with less cost and resources will empower smaller teams. Also, with models like LLaMA being open source and sharing the weights, it’s probable that more businesses will build their own domain-specific LLMs (case-in-point: BloombergGPT).
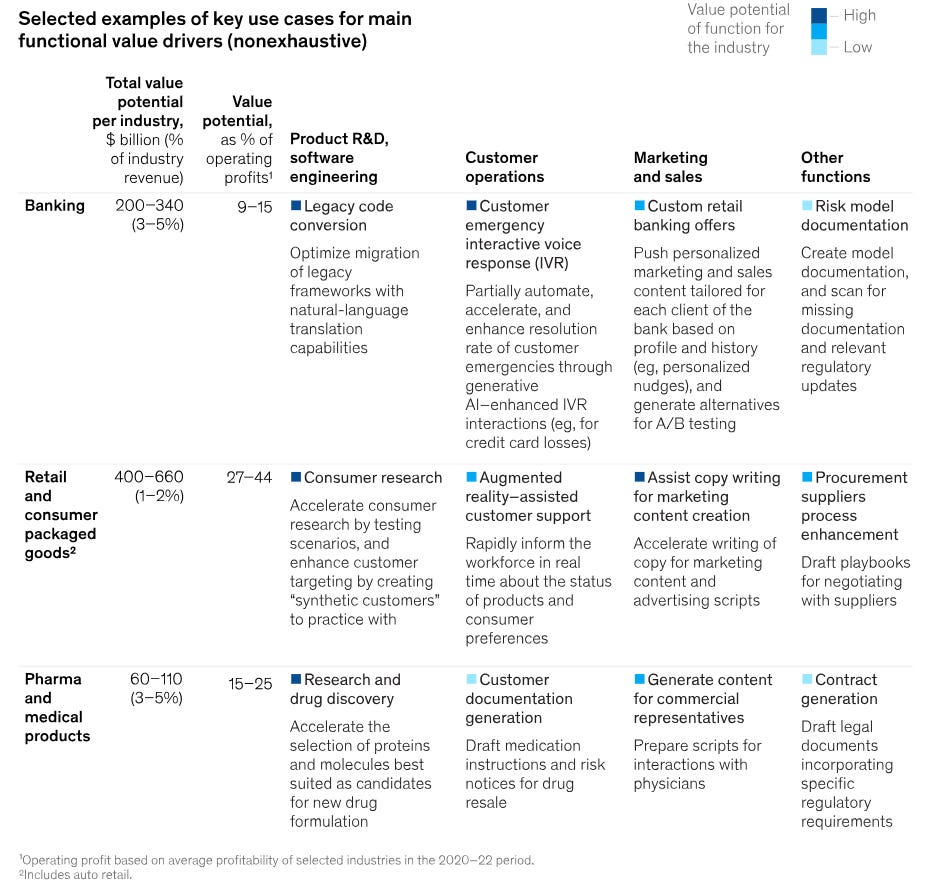
The McKinsey report also highlights how Generative AI is poised to benefit certain industries more than others. High-tech and banking are the two that gain the most. The use cases for every industry will be hugely different. In any case, however, Generative AI solutions or other natural language processing applications will enhance productivity, innovation, and revenue.
2. Hyper-Personalization
AI is typically associated with generalized, one-size-fits-all responses. But Generative AI is being used primarily for its hyper-personalization ability. Every response is tailored to the user’s/customer’s preferences. Applications in this domain include Typeface AI, PlayHT2.0 for customer service, and Sefi AI for content gamification amongst others.
The Generative AI market is ripe with such applications providing a way for businesses to personalize everything from customer service to workflows and management. Even bigger corporations like to personalize user feeds and recommendations. Apps made for writing make business writing customized for businesses and institutes, based on their communicative style.
3. Data Augmentation and Synthesis
Generative AI is enhancing machine learning models through data augmentation and synthesis techniques. Generating synthetic data enriches training datasets, leading to improved model performance and reduced overfitting.
This is particularly valuable in domains with limited real-world data, such as healthcare and finance. A notable example, again, is BloombergGPT which is excellent at handling and augmenting financial data. Qtis AI does the same in diagnosis and medicine.
4. Product Design and Prototyping
Generative AI is revolutionizing product design and prototyping by rapidly generating design iterations. In industries like automotive, fashion, and consumer electronics, it enables creative exploration, accelerates innovation, and minimizes design costs.
Stable Diffusion, Dall-E, and Midjourney, with their multiple iterations, are already supporting designers and creatives in unique ways. These apps have become incredibly sophisticated.
Generative AI has found its place in the art and entertainment industry, producing AI-generated art, music, and literature. However, ethical considerations and copyright issues remain challenges to be addressed in this creative domain.
5. Efficiency and Cost Savings
Generative AI automates time-consuming tasks and reduces manual content creation efforts, resulting in significant cost savings. Streamlining content production workflows is a prime example of how businesses are benefiting from increased efficiency. McKinsey predicts that GenAI can have a direct impact on the productivity of software engineering, prompting an increased spending of 20-45% in this domain by businesses.
6. The Emergence of Explainable Generative AI
Explainability in AI has gained prominence as organizations seek to understand and trust the decisions made by AI systems. In Generative AI, explainability is crucial for applications in healthcare, finance, and legal domains.
Recent research has focused on developing models that not only generate high-quality content but also provide insights into the decision-making process. Explainable Generative AI aims to demystify black-box models, making them more accessible and accountable.
7. Advancements in Multi-Modal Generative AI
Multi-modal Generative AI trains across modalities, such as text, images, audio, and numerical data. This innovation has vast implications for content generation, storytelling, and interactive experiences. For example, it can enable AI-driven virtual assistants to have more natural and engaging conversations by combining text and speech generation.
Venture capital firms have invested $1.7 billion over the past three years in generative AI technology, mostly concentrated on AI-assisted medical research/medicine (often multimodal) and software coding.
8. AI for Scientific Research
The accuracy of AI-generated material is often questioned, but with the superior training of foundational models, and better Generative AI techniques, they’re now able to generate insights and hypotheses.
They can also analyze complex datasets very quickly and even write papers in a specific and custom style. Researchers use generative models to create realistic simulations of natural processes, such as climate patterns and protein folding, advancing our understanding of the world.
Challenges and Hesitations
Savvy business leaders are already utilizing Generative AI in creative ways. But most of them also feel that the technology is highly underutilized, as demonstrated in the chart above. There’s room for innovation and increased application of GenAI, especially among smaller and midsized businesses.
Things like code generators, writing tools, and image generators can all be built and enhanced using sophisticated fine-tuning techniques or creating models from scratch.
Conclusion
Generative AI accelerates innovation by facilitating rapid prototyping and design iteration. Testing various design possibilities in a shorter time frame has a profound impact on industries like manufacturing, architecture, and technology, enabling faster product development and market entry.
In conclusion, Generative AI has evolved into a versatile technology with a wide range of applications across industries. From improving data quality to enhancing user experiences and driving innovation, Generative AI is at the forefront of technological advancements, reshaping the way businesses operate and researchers conduct experiments. As the field continues to evolve, it holds the promise of even more groundbreaking developments in the future.